Overview
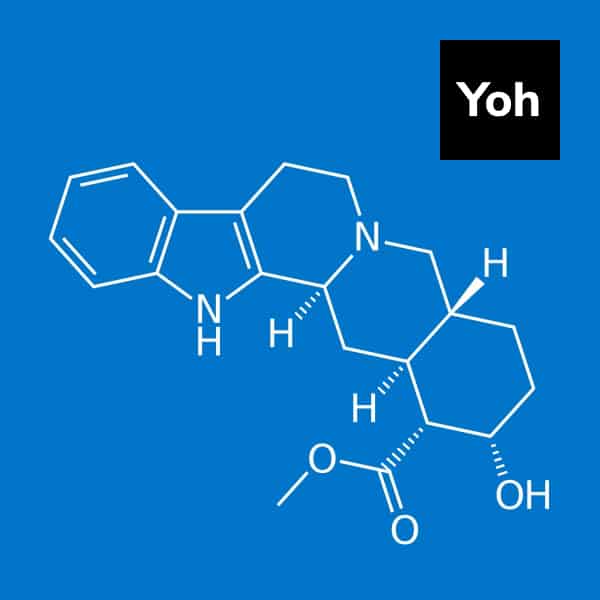
Yohimbine is an alkaloid derived from the bark of the Pausinystalia johimbe tree, an evergreen tree indigenous to western and Central Africa. For centuries, it was employed as an aphrodisiac. Although frequently used before the approval of newer medications to treat erectile dysfunction, current guidelines do not encourage its use. Additionally, yohimbine may produce a variety of adverse effects, interact with a variety of prescription medications, and is not suggested for those with certain medical conditions.
Key Benefits
- Contributes to the alleviation of erectile dysfunction
- Increases libido
- Assists in the circulation of blood and nerve impulses to the penis and vagina
- Supports weight reduction
- Could aid dizzy spells
- Helps improve athletic performance
History of Usage
Yohimbine has been used in the developed world for nearly a century to treat male and female sexual issues. However, Western African cultures have believed in the yohimbine’s medical properties for hundreds of years. It was originally used by women as an aphrodisiac, general tonic, and performance enhancer. Recently, researchers discovered that the bark of the plant includes a number of indole alkaloids that contribute to the creation of nitric oxide, which is necessary for a good male erection.
Yohimbine, on the other hand, has not yet been exposed to rigorous human clinical testing. Although pertinent basic pharmacological and animal research data have been available since the 1990s, dose-response studies are lacking, other routes of administration (e.g., sublingual) have not been examined, and continuous vs “on-demand” delivery has not been considered.
Human trials with a proper design have not been conducted. Due to a lack of proof and the possibility of undesirable side effects, organizations such as the American Urology Association do not advocate yohimbine for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Though yohimbine extracts are illegal in many countries, they are available in hundreds of dietary supplements in the United States.
Biochemistry
The active ingredients in yohimbine are indole alkaloids. Yohimbine inhibits erections by inhibiting alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Additionally, yohimbine stimulates the production of nitric oxide, which dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow to the sexual organs. Nitric oxide also stimulates the release of epinephrine from the adrenal glands.
Recent Trends
Yohimbine is a substance found mostly in male aphrodisiac preparations. Certain supplement producers say that it can also aid in weight loss and athletic performance.
It is available in the following forms: liquid, extract, pill, and powder.
Precautions
- Yohimbine should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Yohimbe should not be taken by individuals with a history of heart illness, hypertension or hypotension, kidney disease, liver disease, or mental health disorders.
- Take with caution if you are taking antidepressant medicine or foods high in tyramine (such as cheese, red wine, or liver), or if you are taking decongestants, diet aids, or phenylpropanolamine-containing products.
- Harvard Medical School researchers tested 49 different yohimbe supplements and concluded that 78% did not clearly disclose the amount of yohimbine included in the product. Supplements that did contain yohimbine were labeled incorrectly. The actual amount of yohimbine in the supplements varied between 28% and 147% of the amount specified on the label.
- Yohimbe is on the Commission E’s (the country’s herbal regulating agency) list of unapproved herbs due to safety and effectiveness concerns.
- The FDA has received many reports of seizures and renal failure associated with the use of yohimbe in the United States.
- Yohimbine has been linked to cardiac arrest and convulsions. Dizziness, nausea, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, elevated blood pressure, and insomnia are all possible side effects of standard doses.
- As little as 40 mg daily can induce significant adverse effects such as altered blood pressure, hallucinations, paralysis, liver, kidney, and cardiac problems, and can even be fatal.
- Anyone considering using yohimbine should visit a healthcare practitioner first.
References
- Susset JG, Tessier CD, Wincze J, Bansal S, Malhotra C, Schwacha MG. Effect of yohimbine hydrochloride on erectile impotence: a double-blind study. J Urol. 1989 Jun;141(6):1360-3. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)41308-5. PMID: 2657105.
- Ernst E, Pittler MH. Yohimbine for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Urol. 1998 Feb;159(2):433-6. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)63942-9. PMID: 9649257.
- Morales A. Yohimbine in erectile dysfunction: the facts. Int J Impot Res. 2000 Mar;12 Suppl 1:S70-74. PMID: 10845767.
- Morales A. Yohimbine in erectile dysfunction: the facts. Int J Impot Res. 2000 Mar;12 Suppl 1:S70-74. PMID: 10845767.
- Cohen PA, Wang YH, Maller G, DeSouza R, Khan IA. Pharmaceutical quantities of yohimbine found in dietary supplements in the USA. Drug Test Anal. 2016 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):357-69. doi: 10.1002/dta.1849. Epub 2015 Sep 22. PMID: 26391406.
- Cohen PA, Wang Y-H, Maller G, et al. Pharmaceutical quantities of yohimbine found in dietary supplements in the USA. Drug Testing and Analysis. 2016;8(3-4):357-369.
- Kearney T, Tu N, Haller C. Adverse drug events associated with yohimbine-containing products: a retrospective review of the California Poison Control System reported cases. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2010;44(6):1022-1029.
- Riley AJ. Yohimbine in the treatment of erectile disorder. Br J Clin Pract. 1994 May-Jun;48(3):133-6. PMID: 8031688.
- Chen Q, Li P, Zhang Z, et al. Analysis of yohimbine alkaloid from Pausinystalia yohimbe by non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci. Jul 2008;31(12):2211-2218.
- Murburg MM, Villacres EC, Ko GN, et al. Effects of yohimbine on human sympathetic nervous system function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Oct 1991;73(4):861-865.
- Ostojic SM. Yohimbine: the effects on body composition and exercise performance in soccer players. Res Sports Med. 2006 Oct-Dec;14(4):289-99. doi: 10.1080/15438620600987106. PMID: 17214405.
- Kucio C, Jonderko K, Piskorska D. Does yohimbine act as a slimming drug? Isr J Med Sci. 1991 Oct;27(10):550-6. PMID: 1955308.