Overview
Glucosamine sulfate is a naturally occurring chemical produced in the body and found in the synovial fluid around the joints. Chondroitin sulfate is also naturally manufactured by the body and is essential for normal joint function. The problem is, as we age, the body produces less, which is why supplementation is needed for optimal joint health. Research demonstrates that glucosamine and chondroitin may be a great alternative to traditional therapies that often have undesirable side effects.
Key Benefits
- Reverses joint deterioration.
- Supports synovial fluid production.
- Helps repair connective tissue.
- Reduces joint pain, joint tenderness, and joint swelling.
- Provides an anti-inflammatory response.
- Provides the building blocks of cartilage.
History of Usage
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) reports that joint pain patterns are increasing.
According to the report, about 91 million individuals in the United States may have some type of arthritis in 2018, and that figure is likely to continue rising. Additionally, it is estimated that millions of men and women worldwide are at risk for developing joint health problems associated with the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, especially in the knees, hip and spine.
Most doctors have said there is little they can do to stop or slow down the onset of bone and joint disorders. However, because of the numerous studies that show glucosamine and chondroitin reduce symptoms of arthritis, and can even repair some of the damage that has already occurred, more and more doctors are recommending the supplements
Biochemistry
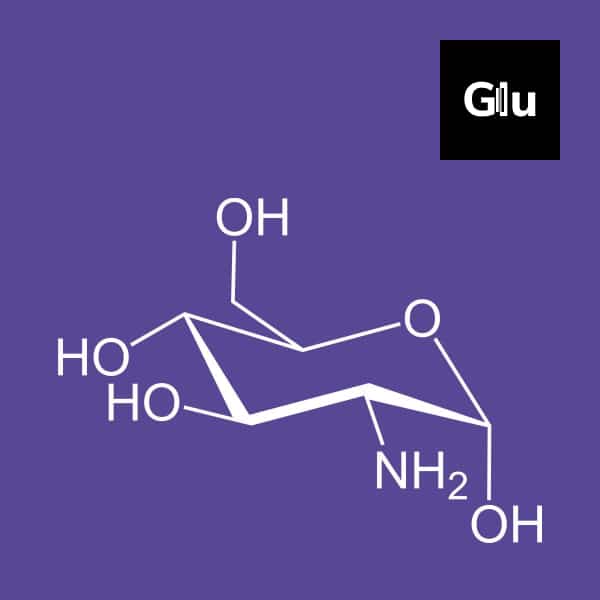
Glucosamine is a kind of amino sugar that serves as a precursor for protein and lipid glycosylation. It is a structural component of chitosan and chitin, two polysaccharides. It is made up of sugars, N-acetylgalactosamine, and glucuronic acid in an alternating chain. It is composed of an alternating chain of sugars, N-acetylgalactosamine, and glucuronic acid. Both glucosamine and chondroitin stimulate the formation of glucosaminoglycans, a natural lubricant and shock absorber that helps your joints to move freely and painlessly.
Glucosamine supplies the precursors for the synthesis of large water-binding molecules required for cartilage development. It aids in the attraction and retention of water, which is necessary for cartilage’s flexibility and fluidity. Additionally, glucosamine stimulates sulfur absorption into cartilage, therefore enhancing its strength and durability.
Chondroitin is involved in a variety of processes involved in connective tissue production. When hydrated, it generates osmotic pressure, which enhances synovial cartilage’s compressive resistance. Additionally, it promotes the synthesis of collagen and proteoglycan and prevents the synovium—the soft tissue that fills the gaps of joints, tendon sheaths, and bursae—from being destroyed by enzymes. The synovium lines the whole inner surface of the joint, with the exception of cartilage-lined joints.
Recent trends
The joint health market is one of the largest and most important in the natural supplements industry. Usage of glucosamine and chondroitin supplements in recent trends has increased tremendously, and so has its demand among older and younger individuals.
The joint category has traditionally been aimed towards an older population. However, energetic, young individuals who wish to preserve joint flexibility, avoid future issues, and obtain respite from strenuous exercises and activities, as well as sitting for long periods of time at their workstations, are increasingly purchasing joint health products.
Glucosamine is the name given to a family of amino acids, which includes both the precursors and the final compound of all known natural health supplements. Its recognition as one of the important amino acids has led to its recognition in the medical world, too.
Glucosamine health supplements can be used as adjunctive therapy along with certain medications to fight joint pain and stiffness. These supplements are obtainable over the counter, so they can be used by anyone who needs them. These supplements are used for various disorders, like arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, etc.
Precautions
Usage of glucosamine health supplements is associated with various risks and advantages. Adverse effects that can occur due to over-dosage are gastrointestinal disturbances, gas, constipation, nausea, diarrhea, insomnia, fatigue, headaches, liver and kidney problems, abnormal bleeding, etc. However, in most cases, these side effects subside after consumption ceases.
In very few cases where the dosage exceeds the normal limits, serious complications can result. Most of these risks can be reduced by a consultation with a medical professional before starting any supplement.
Resources
- Madaleno FO, Santos BA, Araújo VL, Oliveira VC, Resende RA Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in former athletes: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2018 Apr 4. Pie: S1413-3555(17)30627-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2018.03.012
- Bertin, P, Taieb C. NSAID-sparing effect of glucosamine hydrochloride in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an analysis of data from a French database. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Feb;30(2):271-7. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.855184. Epub 2013 Nov 5.
- Jamialahmadi K, Arasteh O, Matbou Riahi M, Mehri S, Riahi-Zanjani B, Karimi G. Protective effects of glucosamine hydrochloride against free radical-induced erythrocytes damage. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;38(1):212-9. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.05.018. Epub 2014 Jun 7.
- Daniel O. Clegg, M.D., Domenic J. Reda, Ph.D. et al. Glucosamine, Chondroitin Sulfate, and the Two in Combination for Painful Knee Osteoarthritis February 23, 2006 N Engl J Med 2006; 354:795-808 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa052771